publications
publications in reversed chronological order.
2024
-
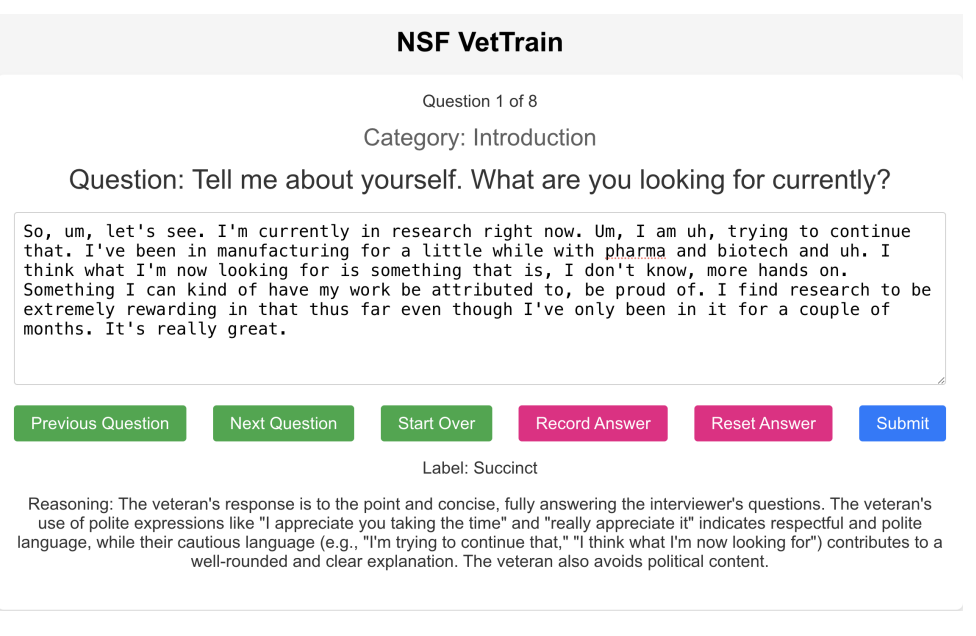 An AI-Powered Interactive Interface to Enhance Accessibility of Interview Training for Military VeteransRakesh Chowdary Yarlagadda, Pranjal Aggarwal, Vaibhav Jamadagni, and 4 more authorsIn Companion Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, San Jose, Costa Rica, 2024
An AI-Powered Interactive Interface to Enhance Accessibility of Interview Training for Military VeteransRakesh Chowdary Yarlagadda, Pranjal Aggarwal, Vaibhav Jamadagni, and 4 more authorsIn Companion Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, San Jose, Costa Rica, 2024This demonstration paper presents an artificial intelligence (AI)-powered interactive interface designed to enhance interview training for military veterans transitioning to civilian jobs. The interface uses large language models (LLMs) to provide real-time feedback on veterans’ responses to common interview questions, classifying answers as under-explained, succinct, comprehensive, or over-explained. The system further offers a justification of its decision, potentially enhancing the user’s understanding of their responses and identifying areas for improvement. This tool aims to bridge the gap between military and civilian employment, addressing unique challenges faced by veterans and potentially extending to other sensitive groups in future applications.
@inproceedings{10.1145/3686215.3688371, author = {Yarlagadda, Rakesh Chowdary and Aggarwal, Pranjal and Jamadagni, Vaibhav and Mahajani, Ghritachi and Malasani, Pavan Kumar and Nirjhar, Ehsanul Haque and Chaspari, Theodora}, title = {An AI-Powered Interactive Interface to Enhance Accessibility of Interview Training for Military Veterans}, series = {ICMI Companion '24}, year = {2024}, address = {New York, NY, USA}, pages = {82-84}, publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery}, doi = {10.1145/3686215.3688371}, isbn = {9798400704635}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3686215.3688371}, booktitle = {Companion Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Multimodal Interaction}, numpages = {3}, keywords = {Interview training, interactive interface, language, large language models, speech}, location = {San Jose, Costa Rica}, acceptance = {Accepted}, } -
 CUNLP at SemEval-2024 Task 8: Classify Human and AI Generated TextPranjal Aggarwal and Deepanshu SachdevaIn Proceedings of the 18th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation, Jun 2024
CUNLP at SemEval-2024 Task 8: Classify Human and AI Generated TextPranjal Aggarwal and Deepanshu SachdevaIn Proceedings of the 18th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation, Jun 2024This task is a sub-part of SemEval-2024 competition which aims to classify AI vs Human Generated Text. In this paper we have experimented on an approach to automatically classify an artificially generated text and a human written text. With the advent of generative models like GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 it has become increasingly necessary to classify between the two texts due to various applications like detecting plagiarism and in tasks like fake news detection that can heavily impact real world problems, for instance stock manipulation through AI generated news articles. To achieve this, we start by using some basic models like Logistic Regression and move our way up to more complex models like transformers and GPTs for classification. This is a binary classification task where the label 1 represents AI generated text and 0 represents human generated text. The dataset was given in JSON style format which was converted to comma separated file (CSV) for better processing using the pandas library in Python as CSV files provides more readability than JSON format files. Approaches like Bagging Classifier and Voting classifier were also used.
@inproceedings{CUNLPsemeval2024task8, title = {{CUNLP} at {SemEval}-2024 Task 8: Classify Human and AI Generated Text}, author = {Aggarwal, Pranjal and Sachdeva, Deepanshu}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the 18th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation}, series = {SemEval 2024}, year = {2024}, address = {Mexico City, Mexico}, month = jun, pages = {1--6}, doi = {10.18653/v1/2024.semeval-1.1}, acceptance = {Published}, }
2023
-
 Tldsmi: Genetic Algorithm Based Network for Text Localization in Distorted Social Media ImagesShivakumara Palaiahnakote, C Pavan Kumar, Pranjal Aggarwal, and 4 more authorsAvailable at SSRN 4348525, Jun 2023
Tldsmi: Genetic Algorithm Based Network for Text Localization in Distorted Social Media ImagesShivakumara Palaiahnakote, C Pavan Kumar, Pranjal Aggarwal, and 4 more authorsAvailable at SSRN 4348525, Jun 2023This paper presents a novel model for understanding social image content through text localization. For text localization, we explore Maximally Stable Extremal Regions (MSER) for detecting components, that works by clustering pixels having similar properties. The output of component detection includes several non-text components due to degradations of social media images. To select the best components among many, we explore Genetic Algorithm by convolving different kernels with components, which results in a feature matrix which is further fed to EfficientNet for choosing actual text components. Therefore, the proposed model is called Genetic Algorithm based Network for Text Localization in Distorted Social Media Images (TLDSMI). For evaluating text localization, we consider the images of standard dataset of natural scene by uploading and downloading from different social media platforms, namely, WhatsApp, Telegram and Instagram. The effectiveness of our method is shown by testing on original and distorted standard datasets.
@article{palaiahnakote4348525tldsmi, author = {Palaiahnakote, Shivakumara and Kumar, C Pavan and Aggarwal, Pranjal and Sharma, Shubham and Chandana, Pasupuleti and Basavanna, M and Pal, Umapada}, journal = {Available at SSRN 4348525}, title = {Tldsmi: Genetic Algorithm Based Network for Text Localization in Distorted Social Media Images}, doi = {10.2139/ssrn.4348525}, year = {2023}, acceptance = {Submitted} }
2022
-
 Hope Speech Detection on Social Media PlatformsPranjal Aggarwal, Pasupuleti Chandana, Jagrut Nemade, and 3 more authorsIn Cybercrime in Social Media, Jun 2022
Hope Speech Detection on Social Media PlatformsPranjal Aggarwal, Pasupuleti Chandana, Jagrut Nemade, and 3 more authorsIn Cybercrime in Social Media, Jun 2022Ever since personal computers became widely available in the consumer market, the amount of harmful content on the internet has significantly expanded. In simple terms, harmful content is anything online which causes a person distress or harm. It may include hate speech, violent content, threats, non-hope speech, etc. The online content must be positive, uplifting and supportive. Over the past few years, many studies have focused on solving this problem through hate speech detection, but very few focused on identifying hope speech. This paper discusses various machine learning approaches to identify a sentence as Hope Speech, Non-Hope Speech, or a Neutral sentence. The dataset used in the study contains English YouTube comments and is released as a part of the shared task "EACL-2021: Hope Speech Detection for Equality, Diversity, and Inclusion". Initially, the dataset obtained from the shared task had three classes: Hope Speech, non-Hope speech, and not in English; however, upon deeper inspection, we discovered that dataset relabeling is required. A group of undergraduates was hired to help perform the entire dataset’s relabeling task. We experimented with conventional machine learning models (such as Naïve Bayes, logistic regression and support vector machine) and pre-trained models (such as BERT) on relabeled data. According to the experimental results, the relabeled data has achieved a better accuracy for Hope speech identification than the original data set.
@incollection{aggarwalhope, author = {Aggarwal, Pranjal and Chandana, Pasupuleti and Nemade, Jagrut and Sharma, Shubham and Saumya, Sunil and Biradar, Shankar}, booktitle = {Cybercrime in Social Media}, title = {Hope Speech Detection on Social Media Platforms}, pages = {67--84}, publisher = {Chapman and Hall/CRC}, doi = {10.1201/9781003304180-4}, year = {2022}, acceptance = {Accepted} }
2021
-
 Random Decision Forest Approach for Mitigating SQL Injection AttacksPranjal Aggarwal, Akash Kumar, Kshitiz Michael, and 3 more authorsIn IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Computing and Communication Technologies (CONECCT), Bangalore, India , Jun 2021
Random Decision Forest Approach for Mitigating SQL Injection AttacksPranjal Aggarwal, Akash Kumar, Kshitiz Michael, and 3 more authorsIn IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Computing and Communication Technologies (CONECCT), Bangalore, India , Jun 2021The paper was selected as the student best paper
Structured Query Language (SQL) is extensively used for storing, manipulating and retrieving information in the relational database management system. Using SQL statements, attackers will try to gain unauthorized access to databases and launch attacks to modify/retrieve the stored data, such attacks are called as SQL injection attacks. Such SQL Injection (SQLi) attacks tops the list of web application security risks of all the times. Identifying and mitigating the potential SQL attack statements before their execution can prevent SQLi attacks. Various techniques are proposed in the literature to mitigate SQLi attacks. In this paper, a random decision forest approach is introduced to mitigate SQLi attacks. From the experimental results, we can infer that the proposed approach achieves a precision of 97% and an accuracy of 95%.
@inproceedings{9622689sqli, author = {Aggarwal, Pranjal and Kumar, Akash and Michael, Kshitiz and Nemade, Jagrut and Sharma, Shubham and C, Pavan Kumar}, booktitle = {IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Computing and Communication Technologies (CONECCT)}, title = {Random Decision Forest Approach for Mitigating SQL Injection Attacks}, pages = {1-5}, doi = {10.1109/CONECCT52877.2021.9622689}, year = {2021}, dimensions = {true}, location = {Bangalore, India}, acceptance = {Accepted}, acceptance_rate = {7\%} }
